Biological Sciences
The “Y” Files
Paradigm magazine
The Y chromosome has been called the Rodney Dangerfield of the genomic world. New studies suggest it’s time to give the chromosome a little respect.
When the bee stings
HHMI Bulletin
A new study suggests large protein complexes called inflammasomes play a role a key role in the body’s response to venom from bee stings.
Viruses, Vaccines and the “Unstoppable” Ralph Tripp
UGA Research Magazine
Colleagues describe UGA’s Ralph Tripp as “unstoppable.” And he’s set his sites on finding a cure for respiratory syncytial virus, to which virtually every American child is exposed by the age of 2.
Study examines how cells tell each other apart
Whithead Institute
The idea of self vs. nonself may sound more like an existential identity crisis than a question in cellular biology. But to Whitehead Institute Associate Member Andrew Chess, the concept could offer information about how cells tell each other apart, a cellular self-awareness that ensures the correct wiring of neurons in the brain.
Inactive genes may contribute to failure of animals cloned from adults cells, study finds
Whitehead Institute
Only 1 percent to 3 percent of animals cloned from adult cells survive to birth; many die mysteriously very early in development, around the time of implantation. A new study suggests that a set of genes important in early development fails to reactivate in adult, or somatic, cell-derived clones, a finding that could help scientists skirt a major roadblock in cloning.
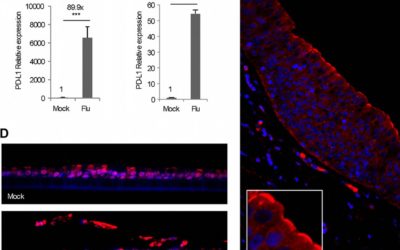
PDL-1 Antibody Could Help Immune System Fight Off Influenza Viral Infection, Study Suggests
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
An antibody that blocks a component of a key signaling pathway in the respiratory airways could help the immune system rid the body of the influenza virus, a new study suggests. The findings not only offer a new approach to treating the flu, but also add new information about how the immune system responds to respiratory viral infections.