News Releases

$1.6 Million Study of Appendicitis Treatment Could Help Children Avoid Surgery
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
In the first study of its kind in the United States, researchers at Nationwide Children’s Hospital will examine the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy alone to treat appendicitis in children, research that could allow patients to avoid a surgery many may not need
Researchers Identify Genetic Mutation Linked to Congenital Heart Disease
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
A mutation in a gene crucial to normal heart development could play a role in some types of congenital heart disease—the most common birth defect in the U.S. The finding could help narrow the search for genes that contribute to this defect, which affects as many as 40,000 newborns a year.
Therapy Slows Onset and Progression of Lou Gehrigs Disease, Study Finds
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Studies of a therapy designed to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) suggest that the treatment dramatically slows onset and progression of the deadly disease, one of the most common neuromuscular disorders in the world.

Rumors of male chromosome’s demise greatly exaggerated, study finds
Whitehead Institute
The Y chromosome has seen its gene supply shrink from more than 1,000 genes when sex chromosomes first evolved, to what scientists once thought was only a handful of genes, a downward trend predicted to continue until the Y disappeared altogether. But two new studies suggest that the rumors of the Y’s demise have been greatly exaggerated.
Study examines how cells tell each other apart
Whithead Institute
The idea of self vs. nonself may sound more like an existential identity crisis than a question in cellular biology. But to Whitehead Institute Associate Member Andrew Chess, the concept could offer information about how cells tell each other apart, a cellular self-awareness that ensures the correct wiring of neurons in the brain.
Inactive genes may contribute to failure of animals cloned from adults cells, study finds
Whitehead Institute
Only 1 percent to 3 percent of animals cloned from adult cells survive to birth; many die mysteriously very early in development, around the time of implantation. A new study suggests that a set of genes important in early development fails to reactivate in adult, or somatic, cell-derived clones, a finding that could help scientists skirt a major roadblock in cloning.
Researchers Identify Potential New Drug for Neurodegenerative Disease
Harvard Medical School
Scientists have discovered a small molecule that helps human cells get rid of the misfolded, disfigured proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative ailments. This potential drug could have applications for other conditions as well.
Efforts to prevent childhood obesity must begin early
Harvard Medical School
Efforts to prevent childhood obesity should begin far earlier than currently thought — perhaps even before birth — especially for minority children, according to a new study that tracked 1,826 women from pregnancy through their children’s first five years of life.

Early warning signs of violence often overlooked, study finds
Ohio University
Many teachers and counselors often overreact to one-time, physical confrontations between kids and overlook nonviolent behaviors that can cause even more damaging, long-term emotional and social problems, according to a new study.
New Crab Trap Reduces Turtle Mortality By Almost 100 Percent, Study Finds
Ohio University
A new crab trap designed by Ohio University researchers has been shown to reduce the mortality rate of turtles accidentally caught in recreational traps by almost 100 percent while increasing the number of crabs caught.
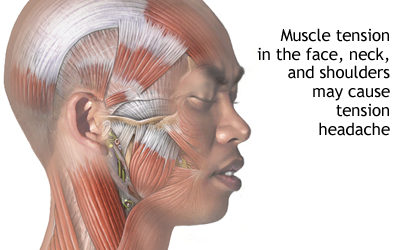
Antidepressant and stress management cut headache pain by half
Ohio University
Findings from a clinical trial of chronic tension headaches suggest a combination of an antidepressant and stress management therapy can cut the frequency of headaches by as much as half.